

Thus, if you are not sure content located Misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such Means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to Information described below to the designated agent listed below. Or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one The minor groove, on the other hand, is the region of double-helix where the distance between the two strands is smallest.

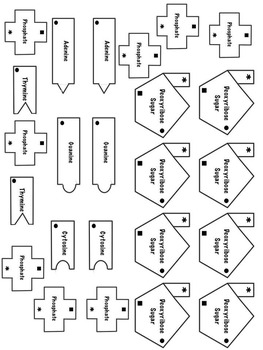
The major groove is the region of the double-helix where the distance between the two DNA strands is largest. One of the characteristics of double-helix is the presence of the major groove and the minor groove. These pentose sugars in the DNA backbone are held together by covalent bonds called phosphodiester bonds therefore, the DNA backbone is held together by covalent bonds.
Double helix definition series#
Recall that the DNA backbone contains a series of pentose sugars that have a phosphate group attached to their 5' carbon. Since it is a noncovalent bond, hydrogen bonds between bases can be broken down by adding energy in the form of heat. The base pairing in the double-helix involves hydrogen bonds, a type of noncovalent bond or intermolecular force. A double-helix can occur in any double-stranded molecule therefore, a double-stranded RNA molecule can also form a double-helix if there is proper base pairing between the strands. This structure arises due to the interaction (hydrogen bonding of base pairs) between the two strands of a DNA molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
